Abstract
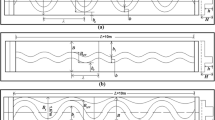
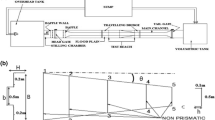
Structures, such as side orifices are used for controlling the flow within a diversion channel or for directing the flow into one. In this study, an equation for estimating discharge coefficient is introduced using “gene expression programming” (GEP). In order to estimate the discharge coefficient, four dimensionless parameters including ratio of depth of flow in main channel to the width of rectangular orifice (Ym/L), Froude number (Fr), the ratio of sill height to the width of rectangular orifice (W/L) and the ratio of the width of the main channel to the width of the rectangular orifice (B/L) are used to present five different models. Therefore, the lacks of effect of each dimensionless parameter on the discharge coefficient predictions are reviewed. The results obtained from the carried out studies indicated that the best model presented in this study estimated the discharge coefficient fairly well with a relative error of 3% against experimental data.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramamurthy, A.S., Tim, U.S., Sarraf, S.: Rectangular lateral orifices in open channels. J. Environ. Eng. 112(2), 292–300 (1986)
Oliveto, G., Biggiero, V., Hager, W.H.: Bottom outlet for sewers. J. Irrig. Drainage Eng. 123(4), 246–252 (1997)
Ghodsian, M.: Flow through side sluice gate. J. Irrig. Drainage Eng. 129(6), 458–463 (2003)
Kra, E.Y., Merkley, G.P.: Mathematical modeling of open-channel velocity profiles for float method calibration. Agric. Water Manag. 70(3), 229–244 (2004)
Amaral, L.G., Righes, A.A., Filho, P.S.S., Costa, R.D.: Automatic regulator for channel flow control on flooded rice. Agric. Water Manag. 75(3), 184–193 (2005)
Lewis, J.W., Wright, S.J., Pribak, M., Sherrill, J.: Bottom slot discharge outlet for combined sewer diversion structure. J. Hydraul. Eng. 137(2), 248–253 (2010)
Gill, M.A.: Flow through side slots. J. Environ. Eng. 113(5), 1047–1057 (1987)
Swamee, P.K., Pathak, S.K., Ali, M.S.: Weir orifice units for uniform flow distribution. ASCE J. Irrig. Drainage Eng. 119(6), 1026–1035 (1993)
Ojha, C.S.P., Subbaiah, D.: Analysis of flow through lateral slot. J. Irrig. Drainage Eng. 123(5), 402–405 (1997)
Prohaska, P.D., Khan, A.A., Kaye, N.B.: Investigation of flow through orifices in riser pipes. J. Irrig. Drainage Eng. 136(5), 340–347 (2010)
Hussain, A., Ahmad, Z., Asawa, G.L.: Discharge characteristics of sharp-crested circular side orifices in open channels. Flow Meas. Instrum. 21(3), 418–424 (2010)
Hussain, A., Ahmad, Z., Asawa, G.L.: Flow through sharp-crested rectangular side orifices under free flow condition in open channels. Agric. Water Manag. 98(10), 1536–1544 (2011)
Ebtehaj, I., Bonakdari, H.: Evaluation of sediment transport in sewer using artificial neural network. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 7(3), 382–392 (2013)
Ebtehaj, I., Bonakdari, H., Zaji, A.H.: A new hybrid decision tree method based on two artificial neural networks for predicting sediment transport in clean pipes. Alexandria Eng. J. 57(3), 1783–1795 (2018)
Ebtehaj, I., Bonakdari, H., Zaji, A.H.: An expert system with radial basis function neural network based on decision trees for predicting sediment transport in sewers. Water Sci. Technol. 74(1), 176–183 (2016)
Ebtehaj, I., Bonakdari, H., Zaji, A.H., Bong, C.H.J., Ab Ghani, A.: Design of a new hybrid artificial neural network method based on decision trees for calculating the Froude number in rigid rectangular channels. J. Hydrol. Hydromechanics 64(3), 252–260 (2016)
Ebtehaj, I., Bonakdari, H.: Performance evaluation of adaptive neural fuzzy inference system for sediment transport in sewers. Water Resour. Manage 28(13), 4765–4779 (2014)
Khoshbin, F., Bonakdari, H., Ashraf Talesh, S.H., Ebtehaj, I., Zaji, A.H., Azimi, H.: Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system multi-objective optimization using the genetic algorithm/singular value decomposition method for modelling the discharge coefficient in rectangular sharp-crested side weirs. Eng. Optim. 48(6), 933–948 (2016)
Sharifipour, M., Bonakdari, H., Zaji, A.H.: Comparison of genetic programming and radial basis function neural network for open-channel junction velocity field prediction. Neural Comput. Appl. 30(3), 855–864 (2016)
Bonakdari, H., Ebtehaj, I., Samui, P., Gharabaghi, B.: Lake water-level fluctuations forecasting using minimax probability machine regression, relevance vector machine, gaussian process regression, and extreme learning machine. Water Resour. Manage 33(11), 3965–3984 (2019)
Shaghaghi, S., Bonakdari, H., Gholami, A., Ebtehaj, I., Zeinolabedini, M.: Comparative analysis of GMDH neural network based on genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization in stable channel design. Appl. Math. Comput. 313, 271–286 (2017)
Bonakdari, H., Ebtehaj, I., Gharabaghi, B., Vafaeifard, M., Akhbari, A.: Calculating the energy consumption of electrocoagulation using a generalized structure group method of data handling integrated with a genetic algorithm and singular value decomposition. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 21(2), 379–393 (2018)
Ebtehaj, I., Bonakdari, H., Zaji, A.H., Azimi, H., Khoshbin, F.: GMDH-type neural network approach for modeling the discharge coefficient of rectangular sharp-crested side weirs. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 18(4), 746–757 (2015)
Ebtehaj, I., Bonakdari, H.: Comparison of genetic algorithm and imperialist competitive algorithms in predicting bed load transport in clean pipe. Water Sci. Technol. 70(10), 1695–1701 (2014)
Ebtehaj, I., Bonakdari, H., Khoshbin, F., Azimi, H.: Pareto genetic design of group method of data handling type neural network for prediction discharge coefficient in rectangular side orifices. Flow Meas. Instrum. 41, 67–74 (2015)
Ebtehaj, I., Bonakdari, H., Zaji, A.H., Azimi, H., Sharifi, A.: Gene expression programming to predict the discharge coefficient in rectangular side weirs. Appl. Soft Comput. 35, 618–628 (2015)
Azamathulla, H.M.: Gene expression programming for prediction of scour depth downstream of sills. J. Hydrol. 460, 156–159 (2012)
Azamathulla, H.M.: Gene-expression programming to predict friction factor for Southern Italian rivers. Neural Comput. Appl. 23(5), 1421–1426 (2013)
Azamathulla, H.M., Ahmad, Z.: Gene-expression programming for transverse mixing coefficient. J. Hydrol. 434, 142–148 (2012)
Guven, A., Azamathulla, H.M.: Gene-expression programming for flip-bucket spillway scour. Water Sci. Technol. 65(11), 1982–1987 (2012)
Koza, J.R.: Genetic Programming: on the Programming of Computers by Means of Natural Selection, vol. 1. MIT Press, Cambridge (1992)
Ferreira, C.: Gene expression programming: a new adaptive algorithm for solving problems. Complex Syst. 13(2), 87–129 (2001)
Legates, D.R., McCabe Jr., G.J.: Evaluating the use of “goodness-of-fit” measures in hydrologic and hydroclimatic model validation. Water Resour. Res. 35(1), 233–241 (1999)
Sudheer, K.P., Jain, S.K.: Radial basis function neural network for modeling rating curves. J. Hydrol. Eng. 8(3), 161–164 (2003)
Garrick, M., Cunnane, C., Nash, J.E.: A criterion of efficiency for rainfall-runoff models. J. Hydrol. 36(3–4), 375–381 (1978)
Hsu, K.L., Gupta, H.V., Sorooshian, S.: Artificial neural network modeling of the rainfall-runoff process. Water Resour. Res. 31(10), 2517–2530 (1995)
Jain, A., Varshney, A.K., Joshi, U.C.: Short-term water demand forecast modelling at IIT Kanpur using artificial neural networks. Water Resour. Manag. 15(5), 299–321 (2001)
Jain, A., Ormsbee, L.E.: Short-term water demand forecast modeling techniques—conventional methods versus AI. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 94(7), 64–72 (2002)
Rajurkar, M.P., Kothyari, U.C., Chaube, U.C.: Modeling of the daily rainfall-runoff relationship with artificial neural network. J. Hydrol. 285(1–4), 96–113 (2004)
Eghbalzadeh, A., Javan, M., Hayati, M., Amini, A.: Discharge prediction of circular and rectangular side orifices using artificial neural networks. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 20(2), 990–996 (2016)
Azimi, H., Shabanlou, S., Ebtehaj, I., Bonakdari, H., Kardar, S.: Combination of computational fluid dynamics, adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system, and genetic algorithm for predicting discharge coefficient of rectangular side orifices. J. Irrig. Drainage Eng. 143(7), 04017015 (2017)
Azimi, A.H., Rajabi, A., Shabanlu, S.: Optimized ANFIS-Genetic algorithm-particle swarm optimization model for estimation of side orifices discharge coefficient. J. Numer. Methods Civ. Eng. 2(4), 27–38 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bonakdari, H., Gharabaghi, B., Ebtehaj, I., Sharifi, A. (2020). A New Approach to Estimate the Discharge Coefficient in Sharp-Crested Rectangular Side Orifices Using Gene Expression Programming. In: Arai, K., Kapoor, S., Bhatia, R. (eds) Intelligent Computing. SAI 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1230. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-52243-8_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-52243-8_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-52242-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-52243-8
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)